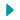
Abuja, 4 June 2024: In recent weeks, Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) inpatient facilities in northern Nigeria have recorded an extraordinary increase in admissions of severely malnourished children with life-threatening complications, with two times more admissions than last year in some locations. This is horrifying as the high influx of patients, and the increase in acute malnutrition that accompanies it, is occurring before the usual peak in July.
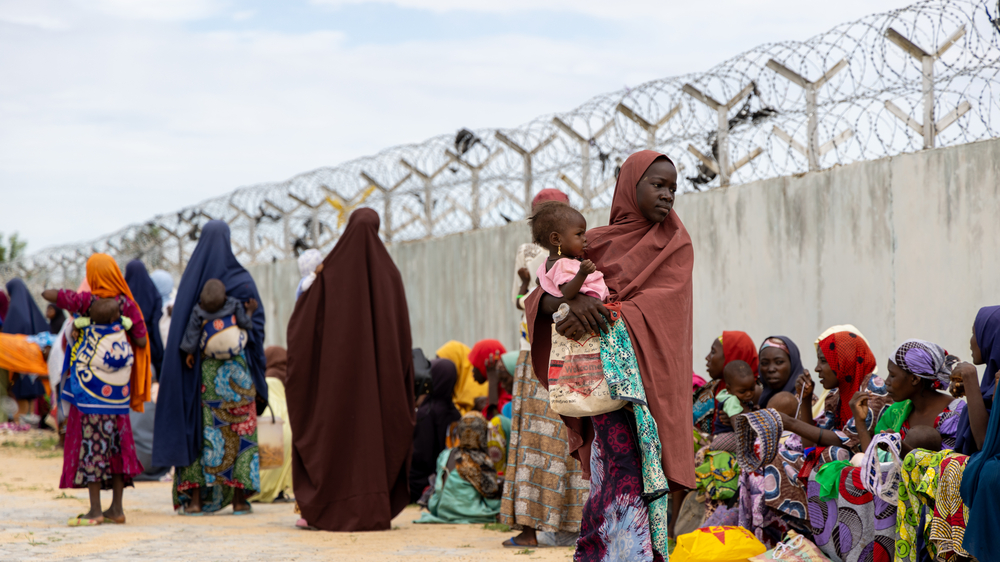

Humanitarian assistance must be urgently scaled up. MSF calls upon the Nigerian authorities, international organisations and donors to take immediate action to diagnose and treat malnourished children to prevent associated complications and deaths, but also to engage in sustained, long-term initiatives to mitigate the underlying causes of this urgent problem.
In April 2024, MSF’s medical team in Maiduguri in northeast Nigeria admitted 1250 severely malnourished children with complications to the inpatient therapeutic feeding centre, doubling the figure for April 2023. Forced to urgently scale up capacity, by the end of May the centre accommodated 350 patients, far surpassing the 200 beds initially designated for the peak malnutrition season in July and August.
Also in the northeast, the MSF-operated facility in Bauchi state’s Kafin Madaki hospital recorded a significant 188 per cent increase in admissions of severely malnourished children during the first three months of 2024 compared to the same period in 2023.
In the northwestern part of the region, in Zamfara state, the inpatient centres in Shinkafi and Zurmi have received up to 30 per cent more admissions in April compared to March. Talata Mafara’s facility saw about 20 per cent increase in the same period. Similarly in April, MSF inpatient facilities in major cities like Kano and Sokoto reported alarming surges, by 75 and 100 per cent respectively. The therapeutic feeding centre in Kebbi state also documented a rise of more than 20 per cent in inpatient admissions from March to April 2024.
Despite the alarming situation, the overall humanitarian response remains inadequate. Other non-profit organisations active in the north are also overwhelmed. The United Nations and Nigerian authorities issued an urgent appeal in May for $306.4 million to address the pressing nutritional needs in Borno, Adamawa, and Yobe states. Yet this will be insufficient, ignoring as it does other parts of northern Nigeria where needs also outweigh the current capacity of the organisations to respond sufficiently.
The catastrophic nutritional situation seen in recent years in northern Nigeria calls for a bigger response. Persistently excluded from the formal humanitarian response, reductions in the already limited funding available for the northwest have also dangerously affected the provision of crucial therapeutic and supplementary food. These supplies were completely unavailable in Zamfara state for the first four months of this year and are now only available in lower quantities. This reduction has meant that it is only possible to provide treatment for more severe malnutrition cases, compromising an effective response that also addresses malnutrition earlier in its progression and avoids exposing children to a higher risk of mortality.
The persistent malnutrition crisis in northern Nigeria stems from a variety of factors such as inflation; food insecurity; insufficient healthcare infrastructure; ongoing security issues, and disease outbreaks worsened by low vaccine coverage.
Tackling acute malnutrition in northern Nigeria requires preventive and curative steps. Establishing and strengthening healthcare facilities and programmes capable of diagnosing and treating malnutrition effectively is an immediate measure needed. Furthermore, reinforcing vaccine programmes that can help stave off vaccine-preventable diseases, enhancing access to nutritious food through agricultural initiatives and food distribution programs, improving water and sanitation situation and raising awareness are key steps.