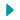
A growing, yet largely ignored, malnutrition crisis is unfolding in northwest Nigeria, which threatens the lives of tens of thousands of children, the medical humanitarian organisation Médecins Sans Frontières /Doctors Without Borders (MSF) warned today. Since January, MSF teams, working in partnership with Nigerian health authorities in five northwestern states, have already treated more than 50,000 children with acute malnutrition, including 7,000 who required hospital care. MSF fears that the situation will soon become untenable without increased lifesaving humanitarian support.
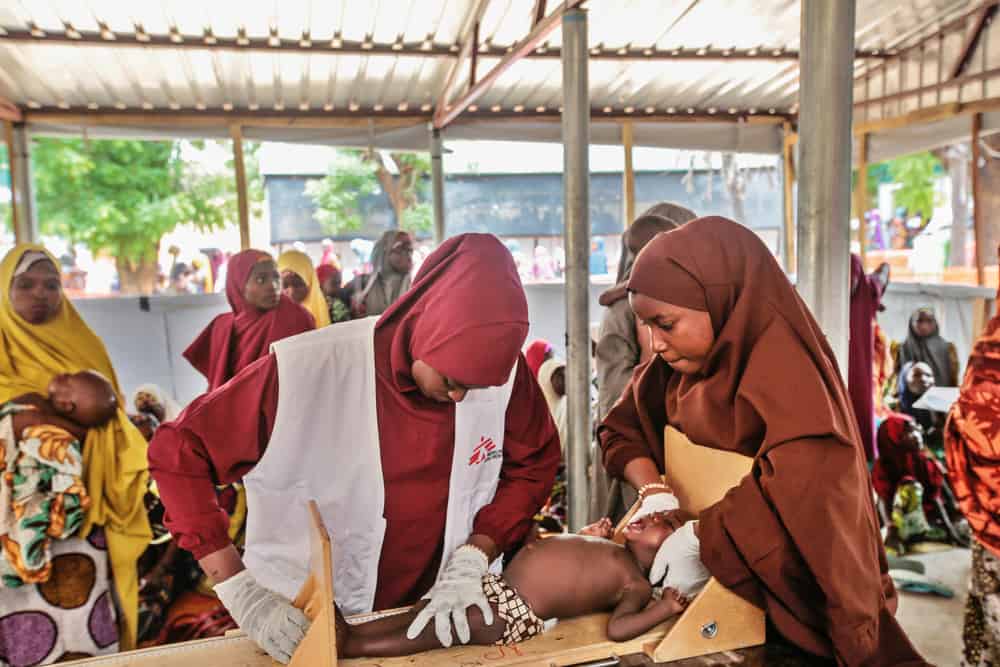
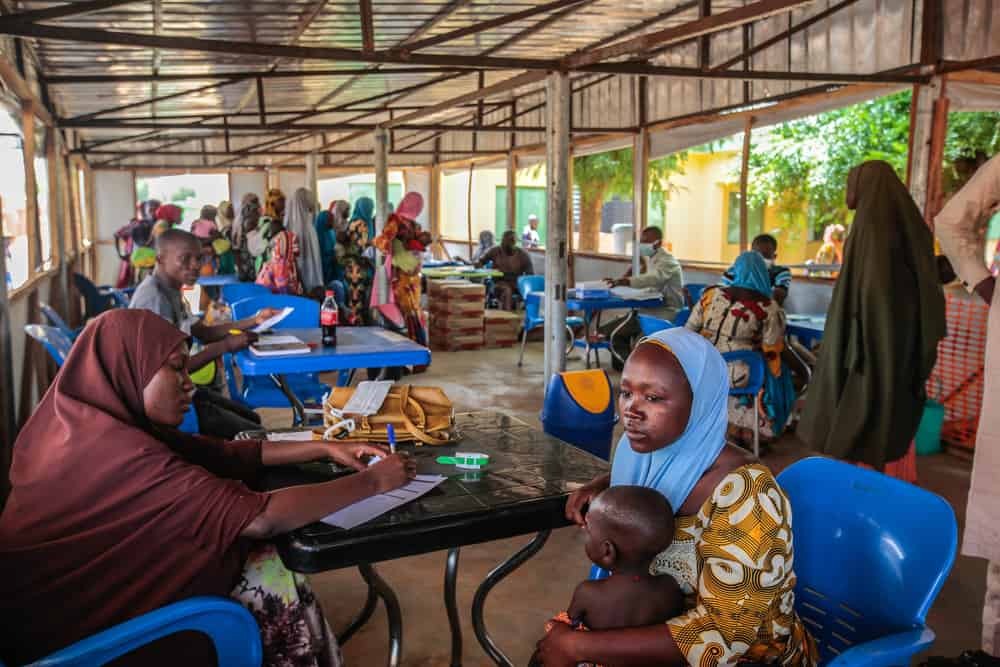


In the area of Gummi, Zamfara state, MSF teams conducted a screening of more than 36,000 children under five years old in June, following a nutrition alert. The results were alarming, as more than half the children were found to be malnourished. Of the total screened children, almost every fourth was severely malnourished and in need of urgent medical care. MSF, in cooperation with the authorities, is immediately launching an emergency response in the area. In Katsina, the teams quickly had to increase their inpatient capacity from 100 to nearly 280 beds in the last few weeks, but the influx of malnourished children was so significant that restricted admission criteria had to be introduced for some of the treatment centres. In Kebbi, where MSF runs an inpatient and two outpatient facilities, about 1,500 malnourished children have been treated since March.
In this chronically food-insecure region, escalating levels of violence have pushed many communities to their limits, including about 500,000 people forced to flee from home[1]. In recent years, armed groups that are locally referred to as ‘bandits’ have intensified attacks, killings, kidnappings, lootings and sexual violence. Many people cannot farm, cattle are stolen, and markets and trade are disrupted amidst soaring staple food prices – which remain above the five-year average in most Nigerian markets[2] – in an already fragile health context.

If the current humanitarian assistance lags far behind in northwest Nigeria, that’s partly because the UN have failed to include the region in its humanitarian response plan for the country for the current year, which primarily focuses on the critical situation in the Northeast. As a result, many organisations are struggling to follow up on assessments and secure funding to implement lifesaving support in northwest Nigeria, despite the known acute needs.
[1] IOM Displacement Tracking Matrix, December 2021
[2] Famine Early Warning System Network (Fews Net) – Nigeria: Key message update, May 2022
While fighting against malnutrition in Zamfara since 2015, MSF has provided additional capacity in Katsina, Kebbi, Sokoto, Zamfara and Kano states in 2021 and 2022. Today, MSF is running 25 outpatient and 8 inpatient malnutrition services across the five states, and MSF teams treated close to 31,000 children with severe acute malnutrition in 2021. MSF also recently raised the alarm on the situation in Maiduguri, Borno state, where our inpatient malnutrition centre is overwhelmed with high numbers of patients – 2,199 children from January to June, representing a 50 per cent increase compared to the same period last year.